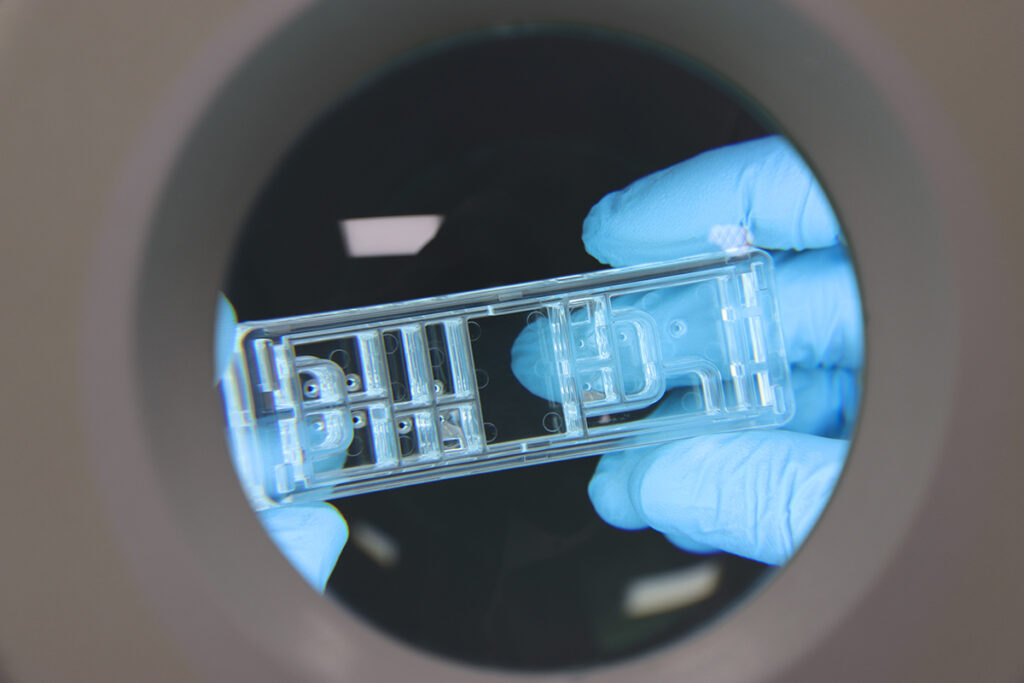
Injection molding microfluidics process definition
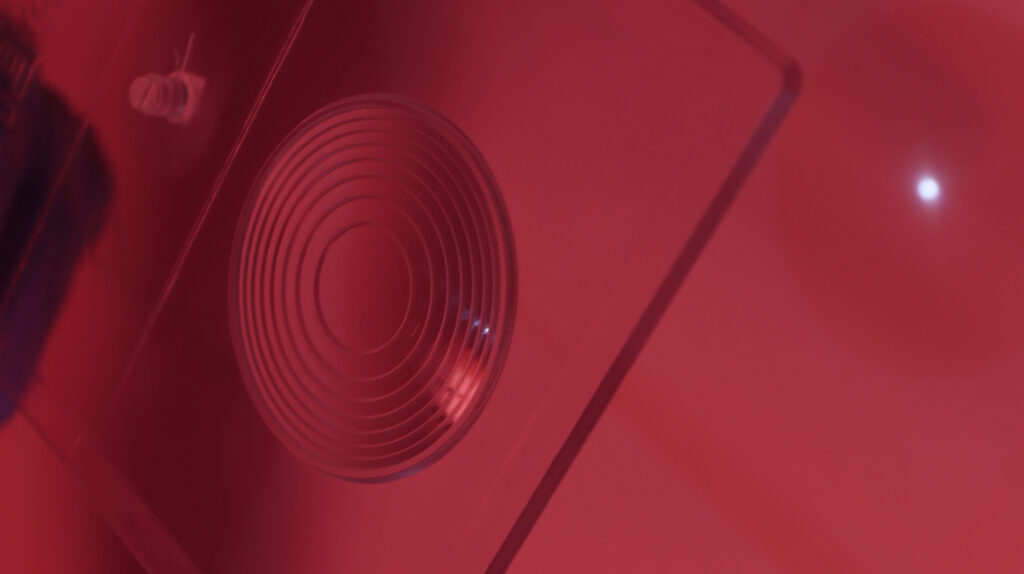

In applications involving low stress, thin walls, and microstructure replication, achieving the desired results heavily relies on precisely setting the injection process type based on scientific principles. Several parameters significantly impact the injection of these parts, with some, such as injection speed curve or barrel temperatures, being particularly critical. However, this analysis focuses on mold temperature and compaction phase methods. Various options exist in this regard:
Optimal replication via isothermal cooling and screw compacting
- This is the standard method for general purpouse components, some hundreds of microns channels and above 1,2mm parts can easily be achieved with good cycle times. It is the easiest process for multicavity operations.
Advanced control: Variothermal cooling and screw compacting for injection molding microfluidics
- When few microns of channels or structures needs to be replicated, variothermal injection molding need to be considered, temperatures much above glass transition is set in the tool not to freeze the polymer when touches the mold surface, when part is filled, the tool is cooled down to be able to eject the part. The mold is compacted by screw force while is cooling down. Few microns structures could be replicated and the effect of weld lines is clearly improved. Thin wall parts injection will be another advantage of this process mode.
Ensuring consistency with isothermal cooling and coining compacting
- Injection compression, specifically isothermal cooling and coining compacting, becomes crucial when minimizing stress in the part and reducing sink marks are priorities. This method applies compression forces during the coining moment, ensuring a constant packing force throughout the part. Adaptations in the tool and machine movements are necessary for this injection mode, and various coining methods can be chosen based on the part’s design and areas requiring compression. This method is particularly preferred for optical parts.
Precision through variothermal cooling and coining compacting in injection molding microfluidics
- Combining variothermal cooling of the mold with compression injection molding offers the best solution for replicating sub-micrometric structures, minimizing stress in parts, and reducing sink marks. This approach amalgamates the benefits of both processes, necessitating careful consideration of tool fabrication to accommodate movements and thermal changes within the tool.
Erreka has experience in all those process settings and could help our customers on process defining, tool manufacturing and injecting the optimized process for each part.

News
We tell you the latest news about ERREKA.

Polymer Science: Driving Innovation in Health and Industry
Polymer science enables the production of devices for a wide range of applications, including biomedical diagnostic (such as point-of-care diagnostics, […]
IVD Raw materials
With the enhancement of medical science and technology, there’s a growing need for real-time diagnostic devices. Many compact systems have […]
From glass chips to polymer chips: revolutionizing microfluidic technology
For many years, glass chips have been integral to biomedical applications, notably in microfluidic technology. However, recent advancements have illuminated […]